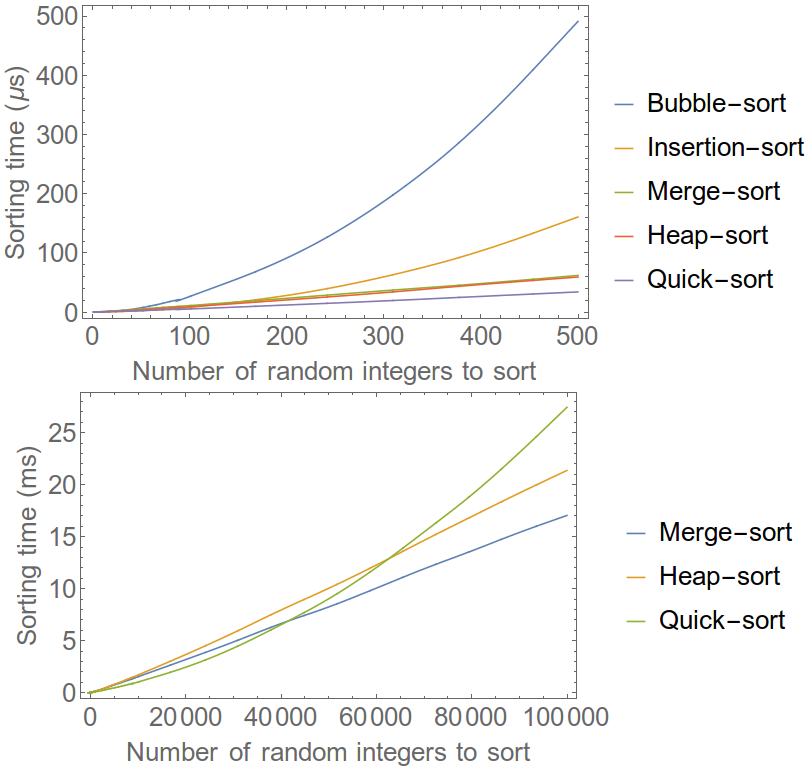
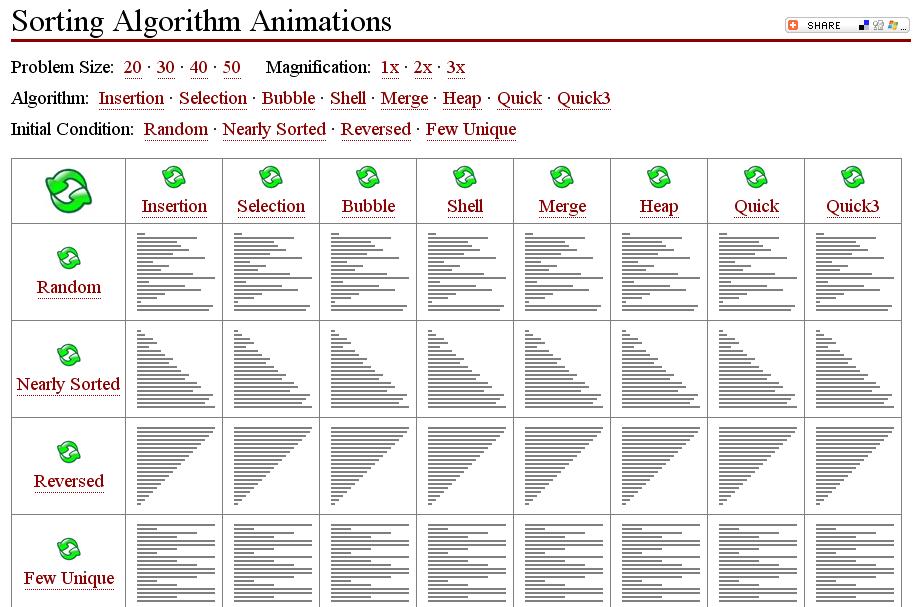
Visual comparison of sorting algorithms’ time complexity
Understanding the efficiency of sorting algorithms is crucial for developers and computer scientists, as the choice of algorithm can greatly impact performance. Here, we explore visual comparisons of various sorting algorithms, focusing on their time complexities and characteristics.
Overview of Sorting Algorithms
Sorting algorithms arrange elements in a specific order, often in ascending or descending numerical order. The efficiency of these algorithms is typically evaluated using time complexity, which describes how the execution time of an algorithm increases as the input size grows. Here, we will provide a visual comparison of several commonly used sorting algorithms.
Common Sorting Algorithms and Their Time Complexities
-
Bubble Sort:
- Best Case: O(n)
- Average Case: O(n²)
- Worst Case: O(n²)
- Simple but inefficient for larger datasets.
-
Selection Sort:
- Best Case: O(n²)
- Average Case: O(n²)
- Worst Case: O(n²)
- More efficient than bubble sort for larger arrays.
-
Insertion Sort:
- Best Case: O(n)
- Average Case: O(n²)
- Worst Case: O(n²)
- Efficient for small data sets and mostly sorted arrays.
-
Merge Sort:
- Best Case: O(n log n)
- Average Case: O(n log n)
- Worst Case: O(n log n)
- Efficient for large data sets with guaranteed performance.
-
Quick Sort:
- Best Case: O(n log n)
- Average Case: O(n log n)
- Worst Case: O(n²)
- Generally faster in practice than other O(n log n) algorithms.
-
Heap Sort:
- Best Case: O(n log n)
- Average Case: O(n log n)
- Worst Case: O(n log n)
- Useful when memory usage is constrained.
-
Counting Sort:
- Best Case: O(n + k)
- Average Case: O(n + k)
- Worst Case: O(n + k)
- Very efficient for sorting a range of integers.
Visual Comparisons of Time Complexity
Visual aids can significantly enhance our understanding of the differences between sorting algorithms. Below are some informative visuals that illustrate the time complexities associated with various sorting methods.
Visualization Resources
-
Sorting Algorithms Time Complexity Comparison
Time complexity comparison across different algorithms (Source: LAMFO) -
Comparison of Sorting Algorithms

Visual representation of various sorting algorithms and their efficiency (Source: AfterAcademy) -
Time Comparison of Quick Sort, Insertion Sort, and Bubble Sort

Comparative analysis of specific sorting algorithms' time complexities (Source: Vinayak Garg) -
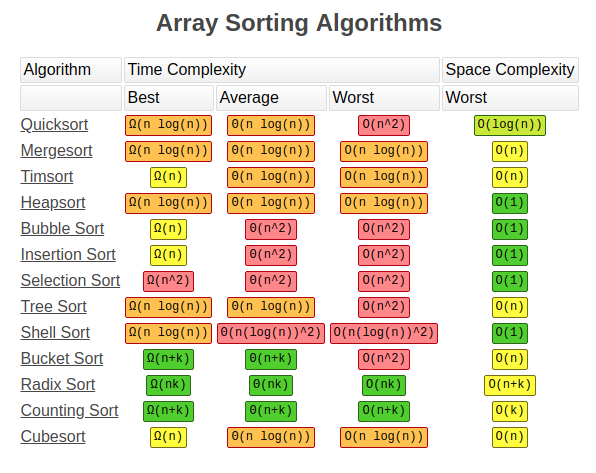
Space and Time Complexity of Sorting Algorithms

Detailed view of time and space complexities for commonly used sorting algorithms (Source: CSEStack)
These visuals clearly depict the theoretical performance of each algorithm under varying conditions and can serve as a quick reference when choosing the appropriate sorting method based on the specific requirements of an application.
Conclusion
Understanding sorting algorithms' time complexities is fundamental in optimizing code and improving application performance. By analyzing visuals like those provided, developers can make informed decisions about which sorting algorithms to implement. Always consider the specifics of your data set and the context of your application when selecting a sorting algorithm. For further insights, you might want to delve into algorithm implementation algorithms or explore advanced techniques like Randomized Quick Sort or Tim Sort.